Germinal Stage on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Human embryonic development, or human embryogenesis, is the development and formation of the human
Human embryonic development, or human embryogenesis, is the development and formation of the human
 The beginning of the cleavage process is marked when the zygote divides through
The beginning of the cleavage process is marked when the zygote divides through
 Cleavage itself is the first stage in
Cleavage itself is the first stage in
 After
After


 The
The

 Following gastrulation, the ectoderm gives rise to epithelial and
Following gastrulation, the ectoderm gives rise to epithelial and
 The heart is the first functional organ to develop and starts to beat and pump blood at around 22 days. Cardiac
The heart is the first functional organ to develop and starts to beat and pump blood at around 22 days. Cardiac
 Late in the fourth week, the superior part of the neural tube bends ventrally as the
Late in the fourth week, the superior part of the neural tube bends ventrally as the
File:Didactic model of a human embryonic development 01.jpg, Representing different stages of embryogenesis
File:Didactic model of a human embryonic development 05.jpg, Early stage of the gastrulation process
File:Didactic model of a human embryonic development 03.jpg, Phase of the gastrulation process
File:Didactic model of a human embryonic development 04.jpg, Top of the form of the embryo
File:Didactic model of a human embryonic development 02.jpg, Establishment of embryo medium
File:Sobo 1909 621.png, Spinal cord at five weeks
File:Gray947.png, Head and neck at 32 days
Virtual human embryo
Photo of blastocyst in utero
* Slideshow
In the Womb
{{DEFAULTSORT:Human Embryogenesis Embryology Human biology
embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
. It is characterised by the processes of cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukar ...
and cellular differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular ...
of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, the development of the human body
Development of the human body is the process of growth to maturity. The process begins with fertilization, where an egg released from the ovary of a female is penetrated by a sperm cell from a male. The resulting zygote develops through mitosi ...
entails growth from a one-celled zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicellula ...
to an adult human being
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedality, bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex Human brain, brain. This has enabled the development of ad ...
. Fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Proce ...
occurs when the sperm cell
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, whi ...
successfully enters and fuses
Fuse or FUSE may refer to:
Devices
* Fuse (electrical), a device used in electrical systems to protect against excessive current
** Fuse (automotive), a class of fuses for vehicles
* Fuse (hydraulic), a device used in hydraulic systems to protec ...
with an egg cell
The egg cell, or ovum (plural ova), is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete is ...
(ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form the single cell zygote and the germinal stage of development commences.
Embryonic development in the human, covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal deve ...
.
Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilization. The normal period of gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregna ...
(pregnancy) is about nine months or 40 weeks.
The germinal stage refers to the time from fertilization through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uter ...
. The germinal stage takes around 10 days. During this stage, the zygote begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst
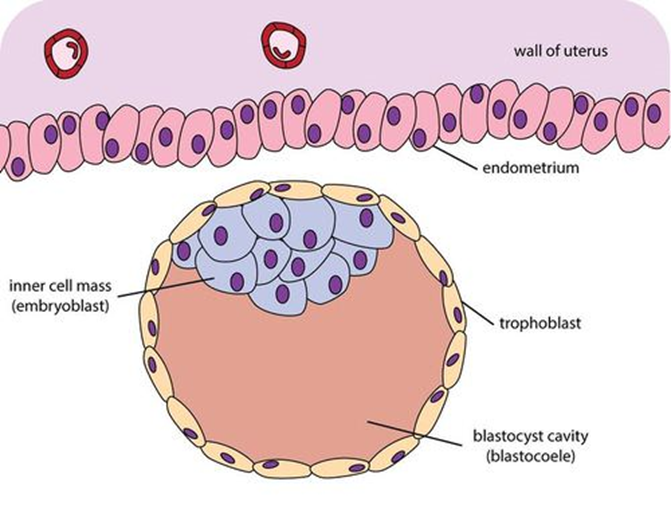
The blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryonic development of mammals. It possesses an inner cell mass (ICM) also known as the ''embryoblast'' which subsequently forms the embryo, and an outer layer of trophoblast cells called the t ...
is then formed and implants in the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uter ...
. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals the blastocyst is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. Be ...
, when the three germ layers
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans (animals that are sister taxa to the sponges) produce two or three pri ...
of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis Histogenesis is the formation of different tissues from undifferentiated cells. These cells are constituents of three primary germ layers, the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. The science of the microscopic structures of the tissues formed wi ...
, and the processes of neurulation
Neurulation refers to the folding process in vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube. The embryo at this stage is termed the neurula.
The process begins when the notochord induces the formati ...
and organogenesis
Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation (the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) form the internal orga ...
follow.
In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. The ...
, cell growth
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell, including both cytoplasmic, nuclear and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis (production of biomolecules or anabolism) is greater than ...
and cellular differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular ...
. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordate
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These fiv ...
s.
Germinal stage
Fertilization
Fertilization takes place when thespermatozoon
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; ; ) is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote is a single cell, with a complete set of chromosomes, t ...
has successfully entered the ovum and the two sets of genetic material carried by the gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce t ...
s fuse together, resulting in the zygote (a single diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively ...
cell). This usually takes place in the ampulla of one of the fallopian tube
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (singular salpinx), are paired tubes in the human female that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In ot ...
s. The zygote contains the combined genetic material carried by both the male and female gametes which consists of the 23 chromosomes from the nucleus of the ovum and the 23 chromosomes from the nucleus of the sperm. The 46 chromosomes undergo changes prior to the mitotic division
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is mainta ...
which leads to the formation of the embryo having two cells.
Successful fertilization is enabled by three processes, which also act as controls to ensure species-specificity. The first is that of chemotaxis
Chemotaxis (from '' chemo-'' + ''taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemica ...
which directs the movement of the sperm towards the ovum. Secondly, an adhesive compatibility between the sperm and the egg occurs. With the sperm adhered to the ovum, the third process of acrosomal reaction
During fertilization, a sperm must first fuse with the plasma membrane and then penetrate the female egg cell to fertilize it. Fusing to the egg cell usually causes little problem, whereas penetrating through the egg's hard shell or extracellular ...
takes place; the front part of the spermatozoan head is capped by an acrosome The acrosome is an organelle that develops over the anterior (front) half of the head in the spermatozoa (sperm cells) of many animals including humans. It is a cap-like structure derived from the Golgi apparatus. In placental mammals the acrosome ...
which contains digestive enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s to break down the zona pellucida
The zona pellucida (plural zonae pellucidae, also egg coat or pellucid zone) is a specialized extracellular matrix that surrounds the plasma membrane of mammalian oocytes. It is a vital constitutive part of the oocyte. The zona pellucida first ...
and allow its entry. The entry of the sperm causes calcium to be released which blocks entry to other sperm cells. A parallel reaction takes place in the ovum called the zona reaction
The cortical reaction is a process initiated during fertilization that prevents polyspermy, the fusion of multiple sperm with one egg. In contrast to the fast block of polyspermy which immediately but temporarily blocks additional sperm from fert ...
. This sees the release of cortical granule
Cortical granules are regulatory secretory organelles (ranging from 0.2 um to 0.6 um in diameter) found within oocytes and are most associated with polyspermy prevention after the event of fertilization. Cortical granules are found among ...
s that release enzymes which digest sperm receptor proteins, thus preventing polyspermy
In biology, polyspermy describes the fertilization of an egg by more than one sperm. Diploid organisms normally contain two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent. The cell resulting from polyspermy, on the other hand, contains three or ...
. The granules also fuse with the plasma membrane and modify the zona pellucida in such a way as to prevent further sperm entry.
Cleavage
 The beginning of the cleavage process is marked when the zygote divides through
The beginning of the cleavage process is marked when the zygote divides through mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is mainta ...
into two cells. This mitosis continues and the first two cells divide into four cells, then into eight cells and so on. Each division takes from 12 to 24 hours. The zygote is large compared to any other cell and undergoes cleavage without any overall increase in size. This means that with each successive subdivision, the ratio of nuclear to cytoplasmic material increases.
Initially, the dividing cells, called blastomeres
In biology, a blastomere is a type of Cell (biology), cell produced by cleavage (embryo), cell division (cleavage) of the zygote after fertilization; blastomeres are an essential part of blastula formation, and blastocyst formation in mammals.
Hum ...
( Greek for sprout), are undifferentiated and aggregated into a sphere enclosed within the zona pellucida
The zona pellucida (plural zonae pellucidae, also egg coat or pellucid zone) is a specialized extracellular matrix that surrounds the plasma membrane of mammalian oocytes. It is a vital constitutive part of the oocyte. The zona pellucida first ...
of the ovum. When eight blastomere
In biology, a blastomere is a type of cell produced by cell division (cleavage) of the zygote after fertilization; blastomeres are an essential part of blastula formation, and blastocyst formation in mammals.
Human blastomere characteristics
In h ...
s have formed, they start to compact
Compact as used in politics may refer broadly to a pact or treaty; in more specific cases it may refer to:
* Interstate compact
* Blood compact, an ancient ritual of the Philippines
* Compact government, a type of colonial rule utilized in British ...
. They begin to develop gap junction
Gap junctions are specialized intercellular connections between a multitude of animal cell-types. They directly connect the cytoplasm of two cells, which allows various molecules, ions and electrical impulses to directly pass through a regulate ...
s, enabling them to develop in an integrated way and co-ordinate their response to physiological signals and environmental cues.
When the cells number around sixteen, the solid sphere of cells within the zona pellucida is referred to as a morula
A morula (Latin, ''morus'': mulberry) is an early-stage embryo consisting of a solid ball of cells called blastomeres, contained in mammals, and other animals within the zona pellucida shell. The blastomeres are the daughter cells of the zygote ...
.
Blastulation
 Cleavage itself is the first stage in
Cleavage itself is the first stage in blastulation
Blastulation is the stage in early animal embryonic development that produces the blastula. In mammalian development the blastula develops into the blastocyst with a differentiated inner cell mass and an outer trophectoderm. The blastula (fr ...
, the process of forming the blastocyst
The blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryonic development of mammals. It possesses an inner cell mass (ICM) also known as the ''embryoblast'' which subsequently forms the embryo, and an outer layer of trophoblast cells called the t ...
. Cells differentiate into an outer layer of cells called the trophoblast
The trophoblast (from Greek : to feed; and : germinator) is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after fertilization in humans. They provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the pl ...
, and an inner cell mass
The inner cell mass (ICM) or embryoblast (known as the pluriblast in marsupials) is a structure in the early development of an embryo. It is the mass of cells inside the blastocyst that will eventually give rise to the definitive structures of ...
. With further compaction the individual outer blastomeres, the trophoblasts, become indistinguishable. They are still enclosed within the zona pellucida
The zona pellucida (plural zonae pellucidae, also egg coat or pellucid zone) is a specialized extracellular matrix that surrounds the plasma membrane of mammalian oocytes. It is a vital constitutive part of the oocyte. The zona pellucida first ...
. This compaction serves to make the structure watertight, containing the fluid that the cells will later secrete. The inner mass of cells differentiate to become embryoblast
The inner cell mass (ICM) or embryoblast (known as the pluriblast in marsupials) is a structure in the early development of an embryo. It is the mass of cells inside the blastocyst that will eventually give rise to the definitive structures of t ...
s and polarise at one end. They close together and form gap junction
Gap junctions are specialized intercellular connections between a multitude of animal cell-types. They directly connect the cytoplasm of two cells, which allows various molecules, ions and electrical impulses to directly pass through a regulate ...
s, which facilitate cellular communication. This polarisation leaves a cavity, the blastocoel
The blastocoel (), also spelled blastocoele and blastocele, and also called cleavage cavity, or segmentation cavity is a fluid-filled or yolk-filled cavity that forms in the blastula during very early embryonic development. At this stage in mammals ...
, creating a structure that is now termed the blastocyst. (In animals other than mammals, this is called the blastula
Blastulation is the stage in early animal embryonic development that produces the blastula. In mammalian development the blastula develops into the blastocyst with a differentiated inner cell mass and an outer trophectoderm. The blastula (from ...
). The trophoblasts secrete fluid into the blastocoel. The resulting increase in size of the blastocyst causes it to hatch through the zona pellucida, which then disintegrates. This process is called zona hatching
Implantation (nidation) is the stage in the embryonic development of mammals in which the blastocyst hatches as the embryo, adheres, and invades into the wall of the female's uterus. Implantation is the first stage of gestation, and when successf ...
and it takes place on the sixth day of embryo development, immediately before the implantation process. The hatching of the human embryo is supported by proteases secreted by the cells of the blastocyst, which digest proteins of the zona pellucida, giving rise to a hole. Then, due to the rhythmic expansion and contractions of the blastocyst, an increase of the pressure inside the blastocyst itself occurs, the hole expands and finally the blastocyst can emerge from this rigid envelope.
The inner cell mass will give rise to the pre-embryo
In human embryonic development a pre-embryo is a conceptus before implantation in the uterus.
Pre-embryo in human embryonic development
The word pre-embryo sometimes is used in ethical contexts to refer to a human conceptus at least between fer ...
, the amnion
The amnion is a membrane that closely covers the human and various other embryos when first formed. It fills with amniotic fluid, which causes the amnion to expand and become the amniotic sac that provides a protective environment for the develo ...
, yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac'' is far ...
and allantois
The allantois (plural ''allantoides'' or ''allantoises'') is a hollow sac-like structure filled with clear fluid that forms part of a developing amniote's conceptus (which consists of all embryonic and extraembryonic tissues). It helps the embryo ...
, while the fetal part of the placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mater ...
will form from the outer trophoblast layer. The embryo plus its membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. B ...
s is called the conceptus
A conceptus (from Latin: ''concipere'' to conceive) is an embryo and its appendages (adnexa), the associated membranes, placenta, and umbilical cord; the products of conception or, more broadly, "the product of conception at any point between fert ...
, and by this stage the conceptus has reached the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uter ...
. The zona pellucida ultimately disappears completely, and the now exposed cells of the trophoblast allow the blastocyst to attach itself to the endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional laye ...
, where it will implant.
The formation of the hypoblast
In amniote embryology, the hypoblast, is one of two distinct layers arising from the inner cell mass in the mammalian blastocyst, or from the blastodisc in reptiles and birds. The hypoblast gives rise to the yolk sac, which in turn gives rise to ...
and epiblast
In amniote embryonic development, the epiblast (also known as the primitive ectoderm) is one of two distinct cell layers arising from the inner cell mass in the mammalian blastocyst, or from the blastula in reptiles and birds, the other layer is t ...
, which are the two main layers of the bilaminar germ disc, occurs at the beginning of the second week. Both the embryoblast and the trophoblast will turn into two sub-layers. The inner cells will turn into the hypoblast layer, which will surround the other layer, called the epiblast, and these layers will form the embryonic disc that will develop into the embryo. The trophoblast will also develop two sub-layers: the cytotrophoblast
"Cytotrophoblast" is the name given to both the inner layer of the trophoblast (also called layer of Langhans) or the cells that live there. It is interior to the syncytiotrophoblast and external to the wall of the blastocyst in a developing embryo ...
, which is in front of the syncytiotrophoblast
Syncytiotrophoblast (from the Greek 'syn'- "together"; 'cytio'- "of cells"; 'tropho'- "nutrition"; 'blast'- "bud") is the epithelial covering of the highly vascular embryonic placental villi, which invades the wall of the uterus to establish nut ...
, which in turn lies within the endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional laye ...
. Next, another layer called the exocoelomic membrane or Heuser's membrane will appear and surround the cytotrophoblast, as well as the primitive yolk sac. The syncytiotrophoblast will grow and will enter a phase called lacunar stage, in which some vacuoles will appear and be filled by blood in the following days. The development of the yolk sac starts with the hypoblastic flat cells that form the exocoelomic membrane, which will coat the inner part of the cytotrophoblast to form the primitive yolk sac. An erosion of the endothelial lining of the maternal capillaries by the syncytiotrophoblastic cells results in the formation of the maternal sinusoids from where the blood will begin to penetrate and flow into and through the trophoblastic lacunae to give rise to the uteroplacental circulation. Subsequently, new cells derived from yolk sac will be established between trophoblast and exocoelomic membrane and will give rise to extra-embryonic mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical E ...
, which will form the chorionic cavity
The gestational sac is the large cavity of fluid surrounding the embryo. During early embryogenesis it consists of the extraembryonic coelom, also called the chorionic cavity. The gestational sac is normally contained within the uterus. It is the o ...
.
At the end of the second week of development, some cells of the trophoblast penetrate and form rounded columns into the syncytiotrophoblast. These columns are known as primary villi. At the same time, other migrating cells form into the exocoelomic cavity a new cavity named the secondary or definitive yolk sac, smaller than the primitive yolk sac.
Implantation
 After
After ovulation
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In women, this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilized ...
, the endometrial lining becomes transformed into a secretory lining in preparation of accepting the embryo. It becomes thickened, with its secretory gland
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two ...
s becoming elongated, and is increasingly vascular
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away f ...
. This lining of the uterine cavity (or womb) is now known as the decidua
The decidua is the modified mucosal lining of the uterus (that is, modified endometrium) that forms every month, in preparation for pregnancy. It is shed off each month when there is no fertilised egg to support. The decidua is under the influ ...
, and it produces a great number of large decidual cells
Before the fertilized ovum reaches the uterus, the mucous membrane of the body of the uterus undergoes important changes and is then known as the decidua. The thickness and vascularity of the mucous membrane are greatly increased; its glands are el ...
in its increased interglandular tissue. The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into an outer layer called the trophoblast
The trophoblast (from Greek : to feed; and : germinator) is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after fertilization in humans. They provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the pl ...
. The trophoblast then differentiates into an inner layer, the cytotrophoblast
"Cytotrophoblast" is the name given to both the inner layer of the trophoblast (also called layer of Langhans) or the cells that live there. It is interior to the syncytiotrophoblast and external to the wall of the blastocyst in a developing embryo ...
, and an outer layer, the syncytiotrophoblast
Syncytiotrophoblast (from the Greek 'syn'- "together"; 'cytio'- "of cells"; 'tropho'- "nutrition"; 'blast'- "bud") is the epithelial covering of the highly vascular embryonic placental villi, which invades the wall of the uterus to establish nut ...
. The cytotrophoblast contains cuboidal
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellu ...
epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellula ...
cells and is the source of dividing cells, and the syncytiotrophoblast is a syncytial
A syncytium (; plural syncytia; from Greek: σύν ''syn'' "together" and κύτος ''kytos'' "box, i.e. cell") or symplasm is a multinucleate cell which can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells (i.e., cells with a single nucleus) ...
layer without cell boundaries.
The syncytiotrophoblast implants the blastocyst in the decidual epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
by projections of chorionic villi
Chorionic villi are villi that sprout from the chorion to provide maximal contact area with maternal blood.
They are an essential element in pregnancy from a histomorphologic perspective, and are, by definition, a product of conception. Branche ...
, forming the embryonic part of the placenta. The placenta develops once the blastocyst is implanted, connecting the embryo to the uterine wall. The decidua here is termed the decidua basalis; it lies between the blastocyst and the myometrium
The myometrium is the middle layer of the uterine wall, consisting mainly of uterine smooth muscle cells (also called uterine myocytes) but also of supporting stromal and vascular tissue. Its main function is to induce uterine contractions.
Struc ...
and forms the maternal part of the placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mater ...
. The implantation is assisted by hydrolytic
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysi ...
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s that erode the epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
. The syncytiotrophoblast
Syncytiotrophoblast (from the Greek 'syn'- "together"; 'cytio'- "of cells"; 'tropho'- "nutrition"; 'blast'- "bud") is the epithelial covering of the highly vascular embryonic placental villi, which invades the wall of the uterus to establish nut ...
also produces human chorionic gonadotropin
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone for the maternal recognition of pregnancy produced by trophoblast cells that are surrounding a growing embryo (syncytiotrophoblast initially), which eventually forms the placenta after implantation ...
, a hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
that stimulates the release of progesterone
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the m ...
from the corpus luteum
The corpus luteum (Latin for "yellow body"; plural corpora lutea) is a temporary endocrine structure in female ovaries involved in the production of relatively high levels of progesterone, and moderate levels of estradiol, and inhibin A. It is t ...
. Progesterone enriches the uterus with a thick lining of blood vessels and capillaries so that it can oxygenate and sustain the developing embryo. The uterus liberates sugar from stored glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one o ...
from its cells to nourish the embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
. The villi begin to branch and contain blood vessels of the embryo. Other villi, called terminal or free villi, exchange nutrients. The embryo is joined to the trophoblastic shell by a narrow connecting stalk that develops into the umbilical cord to attach the placenta to the embryo.
Arteries in the decidua are remodelled to increase the maternal blood flow into the intervillous spaces of the placenta, allowing gas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by Diffusion#Diffusion vs. bulk flow, diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liqui ...
and the transfer of nutrients to the embryo. Waste products from the embryo will diffuse across the placenta.
As the syncytiotrophoblast starts to penetrate the uterine wall, the inner cell mass (embryoblast) also develops. The inner cell mass is the source of embryonic stem cells
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type o ...
, which are pluripotent Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
and can develop into any one of the three germ layer cells, and which have the potency to give rise to all the tissues and organs.
Embryonic disc
The embryoblast forms an embryonic disc, which is a bilaminar disc of two layers, an upper layer called theepiblast
In amniote embryonic development, the epiblast (also known as the primitive ectoderm) is one of two distinct cell layers arising from the inner cell mass in the mammalian blastocyst, or from the blastula in reptiles and birds, the other layer is t ...
(primitive ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from t ...
) and a lower layer called the hypoblast
In amniote embryology, the hypoblast, is one of two distinct layers arising from the inner cell mass in the mammalian blastocyst, or from the blastodisc in reptiles and birds. The hypoblast gives rise to the yolk sac, which in turn gives rise to ...
(primitive endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gast ...
). The disc is stretched between what will become the amniotic cavity
The amniotic sac, also called the bag of waters or the membranes, is the sac in which the embryo and later fetus develops in amniotes. It is a thin but tough transparent pair of membranes that hold a developing embryo (and later fetus) until shor ...
and the yolk sac. The epiblast is adjacent to the trophoblast and made of columnar cells; the hypoblast is closest to the blastocyst cavity and made of cuboidal cells. The epiblast migrates away from the trophoblast downwards, forming the amniotic cavity, the lining of which is formed from amnioblasts developed from the epiblast. The hypoblast is pushed down and forms the yolk sac (exocoelomic cavity) lining. Some hypoblast cells migrate along the inner cytotrophoblast lining of the blastocoel, secreting an extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide stru ...
along the way. These hypoblast cells and extracellular matrix are called Heuser's membrane
Heuser's membrane (or the exocoelomic membrane) is a short lived combination of hypoblast cells and extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of ...
(or the exocoelomic membrane), and they cover the blastocoel to form the yolk sac (or exocoelomic cavity). Cells of the hypoblast migrate along the outer edges of this reticulum and form the extraembryonic mesoderm; this disrupts the extraembryonic reticulum. Soon pockets form in the reticulum, which ultimately coalesce to form the chorionic cavity
The gestational sac is the large cavity of fluid surrounding the embryo. During early embryogenesis it consists of the extraembryonic coelom, also called the chorionic cavity. The gestational sac is normally contained within the uterus. It is the o ...
(extraembryonic coelom).
Gastrulation


 The
The primitive streak
The primitive streak is a structure that forms in the early embryo in amniotes. In amphibians the equivalent structure is the blastopore. During early embryonic development, the embryonic disc becomes oval shaped, and then pear-shaped with the ...
, a linear collection of cells formed by the migrating epiblast, appears, and this marks the beginning of gastrulation
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals the blastocyst is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. Be ...
, which takes place around the seventeenth day (week 3) after fertilization. The process of gastrulation reorganises the two-layer embryo into a three-layer embryo, and also gives the embryo its specific head-to-tail, and front-to-back orientation, by way of the primitive streak which establishes bilateral symmetry
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, take the face of a human being which has a pla ...
. A primitive node
The primitive node (or primitive knot) is the organizer for gastrulation in most amniote embryos. In birds it is known as Hensen's node, and in amphibians it is known as the Spemann-Mangold organizer. It is induced by the Nieuwkoop center in am ...
(or primitive knot) forms in front of the primitive streak which is the organiser of neurulation
Neurulation refers to the folding process in vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube. The embryo at this stage is termed the neurula.
The process begins when the notochord induces the formati ...
. A primitive pit forms as a depression in the centre of the primitive node which connects to the notochord
In anatomy, the notochord is a flexible rod which is similar in structure to the stiffer cartilage. If a species has a notochord at any stage of its life cycle (along with 4 other features), it is, by definition, a chordate. The notochord consis ...
which lies directly underneath. The node has arisen from epiblasts of the amniotic cavity floor, and it is this node that induces the formation of the neural plate
The neural plate is a key developmental structure that serves as the basis for the nervous system. Cranial to the primitive node of the embryonic primitive streak, ectodermal tissue thickens and flattens to become the neural plate. The region ante ...
which serves as the basis for the nervous system. The neural plate will form opposite the primitive streak from ectodermal tissue which thickens and flattens into the neural plate. The epiblast in that region moves down into the streak at the location of the primitive pit where the process called ingression, which leads to the formation of the mesoderm takes place. This ingression sees the cells from the epiblast move into the primitive streak in an epithelial-mesenchymal transition; epithelial cells become mesenchymal stem cells, multipotent Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
stromal cells that can differentiate into various cell types. The hypoblast is pushed out of the way and goes on to form the amnion
The amnion is a membrane that closely covers the human and various other embryos when first formed. It fills with amniotic fluid, which causes the amnion to expand and become the amniotic sac that provides a protective environment for the develo ...
. The epiblast keeps moving and forms a second layer, the mesoderm. The epiblast has now differentiated into the three germ layer
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans (animals that are sister taxa to the sponges) produce two or three pr ...
s of the embryo, so that the bilaminar disc is now a trilaminar disc, the gastrula
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals the blastocyst is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. ...
.
The three germ layers are the ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from t ...
, mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical E ...
and endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gast ...
, and are formed as three overlapping flat discs. It is from these three layers that all the structures and organs of the body will be derived through the processes of somitogenesis
Somitogenesis is the process by which somites form. Somites are bilaterally paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm that form along the anterior-posterior axis of the developing embryo in segmented animals. In vertebrates, somites give rise to skeleta ...
, histogenesis Histogenesis is the formation of different tissues from undifferentiated cells. These cells are constituents of three primary germ layers, the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. The science of the microscopic structures of the tissues formed wi ...
and organogenesis
Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation (the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) form the internal orga ...
. The embryonic endoderm is formed by invagination
Invagination is the process of a surface folding in on itself to form a cavity, pouch or tube. In developmental biology, invagination is a mechanism that takes place during gastrulation. This mechanism or cell movement happens mostly in the vegetal ...
of epiblastic cells that migrate to the hypoblast, while the mesoderm is formed by the cells that develop between the epiblast and endoderm. In general, all germ layers will derive from the epiblast. The upper layer of ectoderm will give rise to the outermost layer of skin, central and peripheral nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes th ...
s, eyes
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and conve ...
, inner ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the ...
, and many connective tissues
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is ...
. The middle layer of mesoderm will give rise to the heart and the beginning of the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
as well as the bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
s, muscles
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle ...
and kidneys
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
. The inner layer of endoderm will serve as the starting point for the development of the lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of th ...
, intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans ...
, thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
, pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an end ...
and bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters ...
.
Following ingression, a blastopore
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals the blastocyst is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. Be ...
develops where the cells have ingressed, in one side of the embryo and it deepens to become the archenteron
The primary gut that forms during gastrulation in a developing embryo is known as the archenteron, the gastrocoel or the primitive digestive tube. It develops into the endoderm and mesoderm of an animal.
Formation in sea urchins
As primary mesen ...
, the first formative stage of the gut. As in all deuterostome
Deuterostomia (; in Greek) are animals typically characterized by their anus forming before their mouth during embryonic development. The group's sister clade is Protostomia, animals whose digestive tract development is more varied. Some exampl ...
s, the blastopore becomes the anus
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, d ...
whilst the gut tunnels through the embryo to the other side where the opening becomes the mouth. With a functioning digestive tube, gastrulation is now completed and the next stage of neurulation
Neurulation refers to the folding process in vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube. The embryo at this stage is termed the neurula.
The process begins when the notochord induces the formati ...
can begin.
Neurulation
 Following gastrulation, the ectoderm gives rise to epithelial and
Following gastrulation, the ectoderm gives rise to epithelial and neural tissue
Nervous tissue, also called neural tissue, is the main tissue (biology), tissue component of the nervous system. The nervous system regulates and controls body functions and activity. It consists of two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) com ...
, and the gastrula is now referred to as the neurula
A neurula is a vertebrate embryo at the early stage of development in which neurulation occurs. The neurula stage is preceded by the gastrula stage; consequentially, neurulation is preceded by gastrulation. Neurulation marks the beginning of the p ...
. The neural plate
The neural plate is a key developmental structure that serves as the basis for the nervous system. Cranial to the primitive node of the embryonic primitive streak, ectodermal tissue thickens and flattens to become the neural plate. The region ante ...
that has formed as a thickened plate from the ectoderm, continues to broaden and its ends start to fold upwards as neural folds
The neural fold is a structure that arises during neurulation in the embryonic development of both birds and mammals among other organisms. This structure is associated with primary neurulation, meaning that it forms by the coming together of tiss ...
. Neurulation
Neurulation refers to the folding process in vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube. The embryo at this stage is termed the neurula.
The process begins when the notochord induces the formati ...
refers to this folding process whereby the neural plate is transformed into the neural tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural fold become elevated, a ...
, and this takes place during the fourth week. They fold, along a shallow neural groove
The neural groove is a shallow median groove of the neural plate between the neural folds of an embryo. The neural plate is a thick sheet of ectoderm surrounded on either side by the neural folds, two longitudinal ridges in front of the primitive ...
which has formed as a dividing median line in the neural plate. This deepens as the folds continue to gain height, when they will meet and close together at the neural crest
Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to vertebrates that arise from the embryonic ectoderm germ layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, per ...
. The cells that migrate through the most cranial part of the primitive line form the paraxial mesoderm
Paraxial mesoderm, also known as presomitic or somitic mesoderm is the area of mesoderm in the neurulating embryo that flanks and forms simultaneously with the neural tube. The cells of this region give rise to somites, blocks of tissue running ...
, which will give rise to the somitomeres
In the developing vertebrate embryo, the somitomeres (or somatomeres) are collections of cells that are derived from the loose masses of paraxial mesoderm that are found alongside the developing neural tube. In human embryogenesis they appear towar ...
that in the process of somitogenesis
Somitogenesis is the process by which somites form. Somites are bilaterally paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm that form along the anterior-posterior axis of the developing embryo in segmented animals. In vertebrates, somites give rise to skeleta ...
will differentiate into somite
The somites (outdated term: primitive segments) are a set of bilaterally paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm that form in the embryonic stage of somitogenesis, along the head-to-tail axis in segmented animals. In vertebrates, somites subdivide in ...
s that will form the sclerotome
The somites (outdated term: primitive segments) are a set of bilaterally paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm that form in the embryonic stage of somitogenesis, along the head-to-tail axis in segmented animals. In vertebrates, somites subdivide in ...
s, the syndetome
The somites (outdated term: primitive segments) are a set of bilaterally paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm that form in the embryonic stage of somitogenesis, along the head-to-tail axis in segmented animals. In vertebrates, somites subdivide ...
s, the myotome
A myotome is the group of muscles that a single spinal nerve innervates. Similarly a dermatome is an area of skin that a single nerve innervates with sensory fibers. Myotomes are separated by myosepta (singular: myoseptum). In vertebrate embryoni ...
s and the dermatome Dermatome may refer to:
* Dermatome (anatomy), an area of skin that is supplied by a single pair of dorsal roots
* Dermatome (embryology), the portion of the embryonic paraxial mesoderm, the somite, which gives rise to dermis
* Dermatome (instrument ...
s to form cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck an ...
and bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
, tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
s, dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided i ...
(skin), and muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
. The intermediate mesoderm gives rise to the urogenital tract and consists of cells that migrate from the middle region of the primitive line. Other cells migrate through the caudal part of the primitive line and form the lateral mesoderm, and those cells migrating by the most caudal part contribute to the extraembryonic mesoderm.
The embryonic disc begins flat and round, but eventually elongates to have a wider cephalic part and narrow-shaped caudal end. At the beginning, the primitive line extends in cephalic
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals m ...
direction and 18 days after fertilization returns caudally until it disappears. In the cephalic portion, the germ layer shows specific differentiation at the beginning of the fourth week, while in the caudal portion it occurs at the end of the fourth week. Cranial and caudal neuropore
Neurulation refers to the folding process in vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube. The embryo at this stage is termed the neurula.
The process begins when the notochord induces the forma ...
s become progressively smaller until they close completely (by day 26) forming the neural tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural fold become elevated, a ...
.
Development of organs and organ systems

Organogenesis
Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation (the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) form the internal orga ...
is the development of the organs
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a f ...
that begins during the third to eighth week, and continues until birth. Sometimes full development, as in the lungs, continues after birth. Different organs take part in the development of the many organ system
An organ system is a biological system consisting of a group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions. Each organ has a specialized role in a plant or animal body, and is made up of distinct tissues.
Plants
Plants have ...
s of the body.
Blood
Haematopoietic stem cell
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the very first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within t ...
s that give rise to all the blood cell
A blood cell, also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte, is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), ...
s develop from the mesoderm. The development of blood formation
Haematopoiesis (, from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from hematopoiet ...
takes place in clusters of blood cells, known as blood islands, in the yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac'' is far ...
. Blood islands develop outside the embryo, on the umbilical vesicle, allantois, connecting stalk, and chorion, from mesodermal hemangioblast
Hemangioblasts are the multipotent precursor cells that can differentiate into both hematopoietic stem cells, hematopoietic and endothelial cells. In the mouse embryo, the emergence of blood islands in the yolk sac at embryonic day 7 marks the ons ...
s.
In the centre of a blood island, hemangioblasts form the haematopoietic stem cells that are the precursor to all types of blood cell. In the periphery of a blood island the hemangioblasts differentiate into angioblast
Angioblasts (or vasoformative cells) are embryonic cells from which the endothelium of blood vessels arises. They are derived from embryonic mesoderm. Blood vessels first make their appearance in several scattered vascular areas that are develope ...
s, the precursors to the blood vessels.
Heart and circulatory system
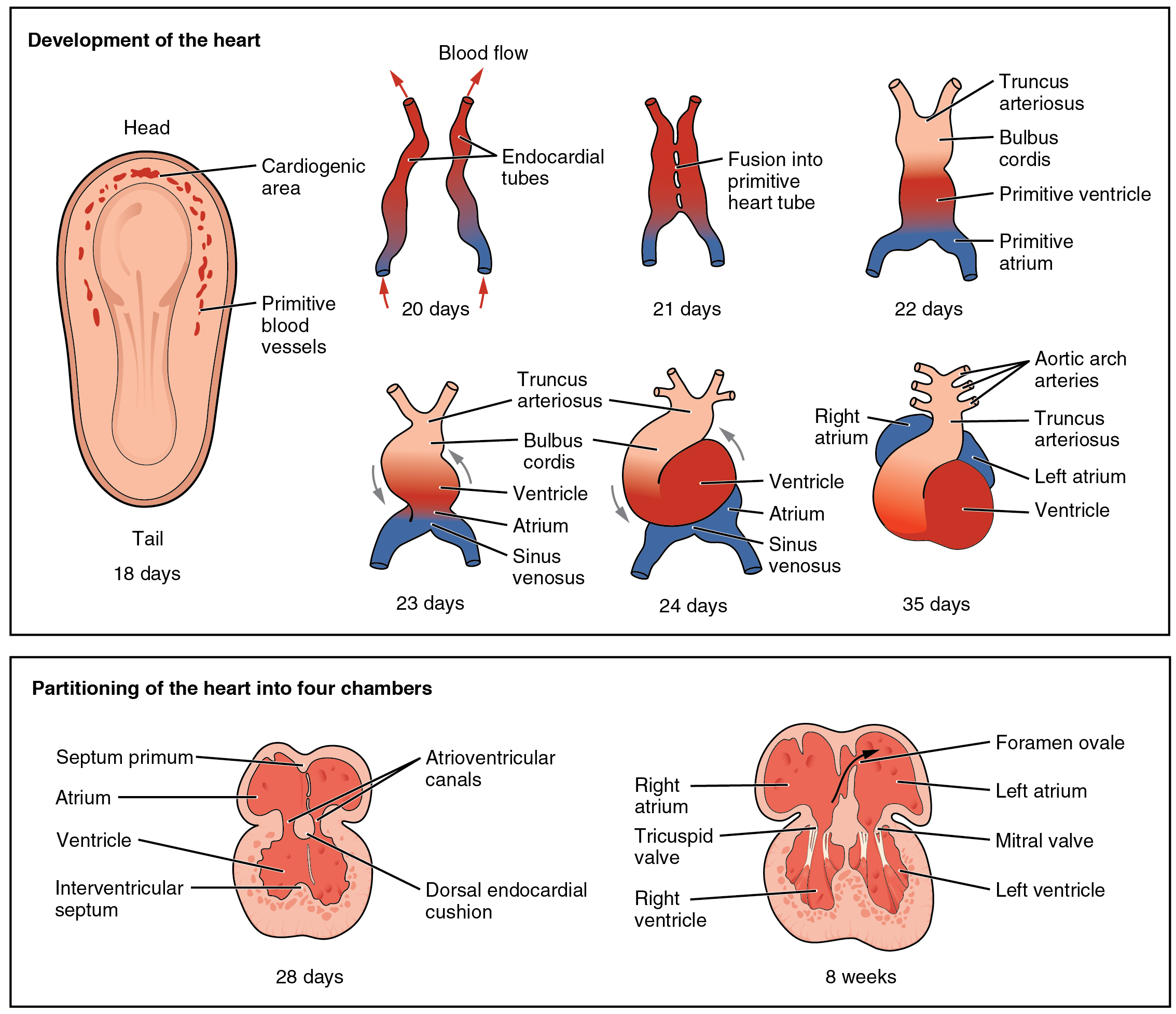
 The heart is the first functional organ to develop and starts to beat and pump blood at around 22 days. Cardiac
The heart is the first functional organ to develop and starts to beat and pump blood at around 22 days. Cardiac myoblast
Myogenesis is the formation of skeletal muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development.
Muscle fibers generally form through the fusion of precursor myoblasts into multinucleated fibers called ''myotubes''. In the early development of ...
s and blood islands
Blood islands are structures around the developing embryo which lead to many different parts of the circulatory system. Blood islands arise external to the developing embryo on the umbilical vesicle, allantois, connecting stalk and chorion. Th ...
in the splanchnopleuric mesenchyme
In the anatomy of an embryo, the splanchnopleuric mesenchyme is a structure created during embryogenesis when the lateral mesodermal germ layer splits into two layers. The inner (or splanchnic) layer adheres to the endoderm, and with it forms ...
on each side of the neural plate
The neural plate is a key developmental structure that serves as the basis for the nervous system. Cranial to the primitive node of the embryonic primitive streak, ectodermal tissue thickens and flattens to become the neural plate. The region ante ...
, give rise to the cardiogenic region
Heart development, also known as cardiogenesis, refers to the prenatal development of the heart. This begins with the formation of two endocardial tubes which merge to form the tubular heart, also called the primitive heart tube. The heart is t ...
.This is a horseshoe-shaped area near to the head of the embryo. By day 19, following cell signalling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
, two strands begin to form as tubes in this region, as a lumen develops within them. These two endocardial tubes The endocardial tubes are paired regions in the embryo that appear in its ventral pole by the middle of the third week of gestation and consist of precursor cells for the development of the embryonic heart. The endocardial heart tubes derive from th ...
grow and by day 21 have migrated towards each other and fused to form a single primitive heart tube, the tubular heart
The tubular heart or primitive heart tube is the earliest stage of heart development.
From the inflow to the outflow, it consists of sinus venosus, primitive atrium, the primitive ventricle, the bulbus cordis, and truncus arteriosus
The truncus ...
. This is enabled by the folding of the embryo which pushes the tubes into the thoracic cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There ...
.
Also at the same time that the endocardial tubes are forming, vasculogenesis
Vasculogenesis is the process of blood vessel formation, occurring by a '' de novo'' production of endothelial cells. It is sometimes paired with angiogenesis, as the first stage of the formation of the vascular network, closely followed by angio ...
(the development of the circulatory system) has begun. This starts on day 18 with cells in the splanchnopleuric mesoderm differentiating into angioblast
Angioblasts (or vasoformative cells) are embryonic cells from which the endothelium of blood vessels arises. They are derived from embryonic mesoderm. Blood vessels first make their appearance in several scattered vascular areas that are develope ...
s that develop into flattened endothelial cells. These join to form small vesicles called angiocysts which join up to form long vessels called angioblastic cords. These cords develop into a pervasive network of plexuses in the formation of the vascular network. This network grows by the additional budding and sprouting of new vessels in the process of angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature by processes of sprouting and splitting ...
. Following vasculogenesis and the development of an early vasculature, a stage of vascular remodelling takes place.
The tubular heart quickly forms five distinct regions. From head to tail, these are the infundibulum An infundibulum (Latin for ''funnel''; plural, ''infundibula'') is a funnel-shaped cavity or organ.
Anatomy
* Brain: the pituitary stalk, also known as the ''infundibulum'' and ''infundibular stalk'', is the connection between the hypothalamus an ...
, bulbus cordis
The bulbus cordis (the bulb of the heart) is a part of the heart development, developing heart that lies ventral to the primitive ventricle after the heart assumes its S-shaped form. The superior end of the bulbus cordis is also called the conotrun ...
, primitive ventricle
The primitive ventricle or embryonic ventricle of the developing heart, together with the bulbus cordis that lies in front of it, gives rise to the left and right ventricles. The primitive ventricle provides the trabeculated parts of the walls, a ...
, primitive atrium
The primitive atrium is a stage in the embryonic development of the human heart. It grows rapidly and partially encircles the bulbus cordis; the groove against which the bulbus cordis lies is the first indication of a division into right and left ...
, and the sinus venosus
The sinus venosus is a large quadrangular cavity which precedes the atrium on the venous side of the chordate heart. In mammals, it exists distinctly only in the embryonic heart, where it is found between the two venae cavae. However, the sinus v ...
. Initially, all venous blood flows into the sinus venosus, and is propelled from tail to head to the truncus arteriosus
The truncus arteriosus is a structure that is present during embryonic development. It is an arterial trunk that originates from both ventricles of the heart that later divides into the aorta and the pulmonary trunk.
Structure
The truncus arterio ...
. This will divide to form the aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes ...
and pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and t ...
; the bulbus cordis will develop into the right (primitive) ventricle; the primitive ventricle will form the left ventricle; the primitive atrium will become the front parts of the left and right atria and their appendages, and the sinus venosus will develop into the posterior part of the right atrium
Atrium may refer to:
Anatomy
* Atrium (heart), an anatomical structure of the heart
* Atrium, the genital structure next to the genital aperture in the reproductive system of gastropods
* Atrium of the ventricular system of the brain
* Pulmona ...
, the sinoatrial node
The sinoatrial node (also known as the sinuatrial node, SA node or sinus node) is an oval shaped region of special cardiac muscle in the upper back wall of the right atrium made up of cells known as pacemaker cells. The sinus node is approximat ...
and the coronary sinus
In anatomy, the coronary sinus () is a collection of veins joined together to form a large vessel that collects blood from the heart muscle ( myocardium). It delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium, as do the superior and inferior ven ...
.
Cardiac looping begins to shape the heart as one of the processes of morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of devel ...
, and this completes by the end of the fourth week. Programmed cell death
Programmed cell death (PCD; sometimes referred to as cellular suicide) is the death of a cell as a result of events inside of a cell, such as apoptosis or autophagy. PCD is carried out in a biological process, which usually confers advantage durin ...
(apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
) at the joining surfaces enables fusion to take place.
In the middle of the fourth week, the sinus venosus receives blood from the three major veins: the vitelline
Vitelline may refer to:
Embryology
* Vitelline arteries, arteries that bring blood to the yolk sac
* Vitelline circulation, the system of blood flowing between an embryo and its yolk sac
* Vitelline cyst, a developmental defect relating to the c ...
, the umbilical and the common cardinal veins.
During the first two months of development, the interatrial septum
The interatrial septum is the wall of tissue that separates the right and left atria of the heart.
Structure
The interatrial septum is a that lies between the left atrium and right atrium of the human heart. The interatrial septum lies at angl ...
begins to form. This septum divides the primitive atrium
The primitive atrium is a stage in the embryonic development of the human heart. It grows rapidly and partially encircles the bulbus cordis; the groove against which the bulbus cordis lies is the first indication of a division into right and left ...
into a right and a left atrium
Atrium may refer to:
Anatomy
* Atrium (heart), an anatomical structure of the heart
* Atrium, the genital structure next to the genital aperture in the reproductive system of gastropods
* Atrium of the ventricular system of the brain
* Pulmona ...
. Firstly it starts as a crescent-shaped piece of tissue which grows downwards as the septum primum
During heart development of a human embryo, the single primitive atrium becomes divided into right and left by a , the septum primum. The septum primum () grows downward into the single atrium.
Development
The gap below it is known as the ostium ...
. The crescent shape prevents the complete closure of the atria allowing blood to be shunted from the right to the left atrium through the opening known as the ostium primum
In the developing heart, the atria are initially open to each other, with the opening known as the primary interatrial foramen or ostium primum (or interatrial foramen primum). The foramen lies beneath the edge of septum primum and the endocardi ...
. This closes with further development of the system but before it does, a second opening (the ostium secundum
The foramen secundum, or ostium secundum is a in the septum primum, a precursor to the interatrial septum of the human heart.
It is not the same as the foramen ovale, which is an opening in the septum secundum.
Development
The foramen secund ...
) begins to form in the upper atrium enabling the continued shunting of blood.
A second septum (the septum secundum
The septum secundum is a muscular flap that is important in heart development. It is semilunar in shape, and grows downward from the upper wall of the atrium immediately to the right of the septum primum and ostium secundum. It is important in the ...
) begins to form to the right of the septum primum. This also leaves a small opening, the foramen ovale which is continuous with the previous opening of the ostium secundum. The septum primum is reduced to a small flap that acts as the valve of the foramen ovale and this remains until its closure at birth. Between the ventricles the septum inferius
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.
The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backwar ...
also forms which develops into the muscular interventricular septum
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.
The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backwar ...
.
Digestive system
The digestive system starts to develop from the third week and by the twelfth week, the organs have correctly positioned themselves.Respiratory system
The respiratory system develops from thelung bud
The lung bud sometimes referred to as the respiratory bud forms from the respiratory diverticulum, an embryological endodermal structure that develops into the respiratory tract organs such as the larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs. It arises from ...
, which appears in the ventral wall of the foregut about four weeks into development. The lung bud forms the trachea and two lateral growths known as the bronchial buds, which enlarge at the beginning of the fifth week to form the left and right main bronchi
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. ...
. These bronchi in turn form secondary (lobar) bronchi; three on the right and two on the left (reflecting the number of lung lobes). Tertiary bronchi form from secondary bronchi.
While the internal lining of the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
originates from the lung bud
The lung bud sometimes referred to as the respiratory bud forms from the respiratory diverticulum, an embryological endodermal structure that develops into the respiratory tract organs such as the larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs. It arises from ...
, its cartilages and muscles originate from the fourth and sixth pharyngeal arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arch ...
es.
Urinary system
Kidneys
Three differentkidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
systems form in the developing embryo: the pronephros
Pronephros is the most basic of the three excretory organs that develop in vertebrates, corresponding to the first stage of kidney development. It is succeeded by the mesonephros, which in fish and amphibians remains as the adult kidney. In amnio ...
, the mesonephros
The mesonephros ( el, middle kidney) is one of three excretory system, excretory organs that develop in vertebrates. It serves as the main excretory organ of aquatic vertebrates and as a temporary kidney in reptiles, birds, and mammals. The mesone ...
and the metanephros Kidney development, or nephrogenesis, describes the embryologic origins of the kidney, a major organ in the urinary system. This article covers a 3 part developmental process that is observed in most reptiles, birds and mammals, including humans. N ...
. Only the metanephros develops into the permanent kidney. All three are derived from the intermediate mesoderm
Intermediate mesoderm or intermediate mesenchyme is a narrow section of the mesoderm (one of the three primary germ layers) located between the paraxial mesoderm and the lateral plate of the developing embryo. The intermediate mesoderm develops i ...
.
= Pronephros
= Thepronephros
Pronephros is the most basic of the three excretory organs that develop in vertebrates, corresponding to the first stage of kidney development. It is succeeded by the mesonephros, which in fish and amphibians remains as the adult kidney. In amnio ...
derives from the intermediate mesoderm in the cervical region. It is not functional and degenerates before the end of the fourth week.
= Mesonephros
= Themesonephros
The mesonephros ( el, middle kidney) is one of three excretory system, excretory organs that develop in vertebrates. It serves as the main excretory organ of aquatic vertebrates and as a temporary kidney in reptiles, birds, and mammals. The mesone ...
derives from intermediate mesoderm in the upper thoracic to upper lumbar segments. Excretory tubules are formed and enter the mesonephric duct
The mesonephric duct (also known as the Wolffian duct, archinephric duct, Leydig's duct or nephric duct) is a paired Organ (anatomy), organ that forms during the embryonic development of humans and other mammals and gives rise to male Sex organ, r ...
, which ends in the cloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, a ...
. The mesonephric duct atrophies in females, but participate in development of the reproductive system
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically ...
in males.
= Metanephros
= The metanephros appears in the fifth week of development. An outgrowth of the mesonephric duct, theureteric bud
The ureteric bud, also known as the metanephric diverticulum, is a protrusion from the mesonephric duct during the development of the urinary and reproductive organs. It later develops into a conduit for urine drainage from the kidneys, which, in c ...
, penetrates metanephric tissue to form the primitive renal pelvis
The renal pelvis or pelvis of the kidney is the funnel-like dilated part of the ureter in the kidney. It is formed by the covnvergence of the major calyces, acting as a funnel for urine flowing from the major calyces to the ureter. It has a mucous ...
, renal calyces
The renal calyces are chambers of the kidney through which urine passes. The minor calyces surround the apex of the renal pyramids. Urine formed in the kidney passes through a renal papilla at the apex into the minor calyx; two or three minor c ...
and renal pyramids
The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the segmental arteries whi ...
. The ureter
The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In a human adult, the ureters are usually long and around in diameter. The ureter is lined by urothelial cells, a type of transitional epit ...
is also formed.
Bladder and urethra
Between the fourth and seventh weeks of development, theurorectal septum
The urorectal septum is an invagination of the cloaca. It divides it into a dorsal part (the hindgut) and a ventral part (the urogenital sinus). It invaginates from cranial to caudal, formed from the endodermal cloaca, and fuses with the cloacal ...
divides the cloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, a ...
into the urogenital sinus
The urogenital sinus is a part of the human body only present in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs. It is the ventral part of the cloaca, formed after the cloaca separates from the anal canal during the fourth to seventh we ...
and the anal canal
The anal canal is the part that connects the rectum to the anus, located below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. It is located within the anal triangle of the perineum, between the right and left ischioanal fossa. As the final functional segment ...
. The upper part of the urogenital sinus forms the bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters ...
, while the lower part forms the urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra con ...
.
Reproductive system
Integumentary system
The superficial layer of theskin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
, the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rele ...
, is derived from the ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from t ...
. The deeper layer, the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided i ...
, is derived from mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every o ...
.
The formation of the epidermis begins in the second month of development and it acquires its definitive arrangement at the end of the fourth month. The ectoderm divides to form a flat layer of cells on the surface known as the periderm. Further division forms the individual layers of the epidermis.
The mesenchyme that will form the dermis is derived from three sources:
* The mesenchyme that forms the dermis in the limbs and body wall derives from the lateral plate mesoderm
The lateral plate mesoderm is the mesoderm that is found at the periphery of the embryo. It is to the side of the paraxial mesoderm, and further to the axial mesoderm. The lateral plate mesoderm is separated from the paraxial mesoderm by a narrow ...
* The mesenchyme that forms the dermis in the back derives from paraxial mesoderm
Paraxial mesoderm, also known as presomitic or somitic mesoderm is the area of mesoderm in the neurulating embryo that flanks and forms simultaneously with the neural tube. The cells of this region give rise to somites, blocks of tissue running ...
* The mesenchyme that forms the dermis in the face and neck derives from neural crest cells
Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to vertebrates that arise from the embryonic ectoderm germ layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, Per ...
Nervous system
cephalic flexure
Three flexures form in the part of the embryonic neural tube that develops into the brain. At four weeks gestational age in the human embryo the neural tube has developed at the cranial end into three swellings – the primary brain vesicles. T ...
at the level of the future midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', " ...
—the mesencephalon
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "m ...
. Above the mesencephalon is the prosencephalon
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the Anatomical terms of location#Directional terms, rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hin ...
(future forebrain) and beneath it is the rhombencephalon
The hindbrain or rhombencephalon or lower brain is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes. Metencephalon ...
(future hindbrain).
Cranial neural crest
The cranial neural crest is one of the four regions of the neural crest.
The cranial neural crest arises in the anterior and populates the face and the pharyngeal arches giving rise to bones, cartilage, nerves and connective tissue. The endocraniu ...
cells migrate to the pharyngeal arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arch ...
es as neural stem cell
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are self-renewing, multipotent cells that firstly generate the radial glial progenitor cells that generate the neurons and glia of the nervous system of all animals during embryonic development. Some neural progenitor ste ...
s, where they develop in the process of neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). It occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs) ...
into neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
s.
The optical vesicle (which eventually becomes the optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
, retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
and iris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
) forms at the basal plate of the prosencephalon. The alar plate
Daminozide—also known as aminozide, Alar, Kylar, SADH, B-995, B-nine, and DMASA,—is a plant growth regulator, a chemical sprayed on fruit to regulate growth, make harvest easier, and keep apples from falling off the trees before they ripen s ...
of the prosencephalon expands to form the cerebral hemispheres (the telencephalon) whilst its basal plate becomes the diencephalon. Finally, the optic vesicle grows to form an optic outgrowth.
Development of physical features
Face and neck
From the third to the eighth week the face and neck develop.Ears
Theinner ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the ...
, middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear).
The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles, which transfer the vibrations of the eardrum into waves in the ...
and outer ear
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle (also pinna) and the ear canal. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum (tympanic membrane).
Structure
Auricle
The ...
have distinct embryological origins.
Inner ear
At about 22 days into development, theectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from t ...
on each side of the rhombencephalon
The hindbrain or rhombencephalon or lower brain is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes. Metencephalon ...
thickens to form otic placode
In embryology, the otic placode is a thickening of the ectoderm on the outer surface of a developing embryo from which the ear develops. The ear, including both the vestibular system and the auditory system, develops from the otic placode beginnin ...
s. These placodes invaginate
Invagination is the process of a surface folding in on itself to form a cavity, pouch or tube. In developmental biology, invagination is a mechanism that takes place during gastrulation. This mechanism or cell movement happens mostly in the vegeta ...
to form otic pit
The auditory pit, also known as the otic pit, is the first rudiment of the internal ear. It appears shortly after that of the eye, in the form of a patch of thickened ectoderm, the auditory plate, over the region of the hind-brain
The hindbrai ...
s, and then otic vesicle
Otic vesicle, or auditory vesicle, consists of either of the two sac-like invaginations formed and subsequently closed off during embryonic development. It is part of the neural ectoderm, which will develop into the membranous labyrinth of the in ...
s. The otic vesicles then form ventral and dorsal components.
The ventral component forms the saccule
The saccule is a bed of sensory cells in the inner ear. It translates head movements into neural impulses for the brain to interpret. The saccule detects linear accelerations and head tilts in the vertical plane. When the head moves verticall ...
and the cochlear duct
The cochlear duct (bounded by the scala media) is an endolymph filled cavity inside the cochlea, located between the tympanic duct and the vestibular duct, separated by the basilar membrane and the vestibular membrane (Reissner's membrane) resp ...
. In the sixth week of development the cochlear duct emerges and penetrates the surrounding mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every o ...
, travelling in a spiral shape until it forms 2.5 turns by the end of the eighth week. The saccule is the remaining part of the ventral component. It remains connected to the cochlear duct via the narrow ductus reuniens.
The dorsal component forms the utricle and semicircular canals
The semicircular canals or semicircular ducts are three semicircular, interconnected tubes located in the innermost part of each ear, the inner ear. The three canals are the horizontal, superior and posterior semicircular canals.
Structure
The ...
.
Middle ear
Thetympanic cavity
The tympanic cavity is a small cavity surrounding the bones of the middle ear. Within it sit the ossicles, three small bones that transmit vibrations used in the detection of sound.
Structure
On its lateral surface, it abuts the external auditory ...
and eustachian tube
In anatomy, the Eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part. In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately long and in d ...
are derived from the first pharyngeal pouch (a cavity lined by endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gast ...
). The distal part of the cleft, the tubotympanic recess, widens to create the tympanic cavity. The proximal part of the cleft remains narrow and creates the eustachian tube.
The bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
s of the middle ear, the ossicles
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three bones in either middle ear that are among the smallest bones in the human body. They serve to transmit sounds from the air to the fluid-filled labyrinth (cochlea). The absence of the auditory ...
, derive from the cartilages of the pharyngeal arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arch ...
es. The malleus
The malleus, or hammer, is a hammer-shaped small bone or ossicle of the middle ear. It connects with the incus, and is attached to the inner surface of the eardrum. The word is Latin for 'hammer' or 'mallet'. It transmits the sound vibrations fro ...
and incus
The ''incus'' (plural incudes) or anvil is a bone in the middle ear. The anvil-shaped small bone is one of three ossicles in the middle ear. The ''incus'' receives vibrations from the ''malleus'', to which it is connected laterally, and transmit ...
derive from the cartilage of the first pharyngeal arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arch ...
, whereas the stapes
The ''stapes'' or stirrup is a bone in the middle ear of humans and other animals which is involved in the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear. This bone is connected to the oval window by its annular ligament, which allows the foo ...
derives from the cartilage of the second pharyngeal arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arc ...
.
Outer ear
Theexternal auditory meatus
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter.
Str ...
develops from the dorsal portion of the first pharyngeal cleft. Six auricular hillocks, which are mesenchymal proliferations at the dorsal aspects of the first and second pharyngeal arches, form the auricle of the ear.
Eyes
The eyes begin to develop from the third week to the tenth week.
Limbs
At the end of the fourth weeklimb development
Limb development in vertebrates is an area of active research in both developmental and evolutionary biology, with much of the latter work focused on the transition from fin to limb.
Limb formation begins in the morphogenetic limb field, as mese ...
begins. Limb bud
The limb bud is a structure formed early in vertebrate limb development. As a result of interactions between the ectoderm and underlying mesoderm, formation occurs roughly around the fourth week of development. In the development of the human em ...
s appear on the ventrolateral aspect of the body. They consist of an outer layer of ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from t ...
and an inner part consisting of mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every o ...
which is derived from the parietal layer of lateral plate mesoderm
The lateral plate mesoderm is the mesoderm that is found at the periphery of the embryo. It is to the side of the paraxial mesoderm, and further to the axial mesoderm. The lateral plate mesoderm is separated from the paraxial mesoderm by a narrow ...
. Ectodermal cells at the distal end of the buds form the apical ectodermal ridge
The apical ectodermal ridge (AER) is a structure that forms from the ectodermal cells at the distal end of each limb bud and acts as a major signaling center to ensure proper development of a limb. After the limb bud induces AER formation, the AE ...
, which creates an area of rapidly proliferating mesenchymal cells known as the progress zone The progress zone is a layer of mesodermal cells immediately beneath the apical ectodermal ridge in the developing limb bud
The limb bud is a structure formed early in vertebrate limb development. As a result of interactions between the ectoderm ...
. Cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck an ...
(some of which ultimately becomes bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
) and muscle develop from the mesenchyme.
Clinical significance
Toxic exposures in the embryonic period can be the cause of majorcongenital malformation
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellect ...
s, since the precursors of the major organ systems are now developing.
Each cell of the preimplantation embryo has the potential to form all of the different cell types in the developing embryo. This cell potency Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
means that some cells can be removed from the preimplantation embryo and the remaining cells will compensate for their absence. This has allowed the development of a technique known as preimplantation genetic diagnosis
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD or PIGD) is the genetic profiling of embryos prior to implantation (as a form of embryo profiling), and sometimes even of oocytes prior to fertilization. PGD is considered in a similar fashion to prenatal ...
, whereby a small number of cells from the preimplantation embryo created by IVF
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating an individual's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) f ...
, can be removed by biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
and subjected to genetic diagnosis. This allows embryos that are not affected by defined genetic diseases to be selected and then transferred to the mother's uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uter ...
.
Sacrococcygeal teratoma
Sacrococcygeal teratoma (SCT) is a type of tumor known as a teratoma that develops at the base of the coccyx (tailbone) and is thought to be primarily derived from remnants of the primitive streak. Sacrococcygeal teratomas are benign 75% of the ...
s, tumours formed from different types of tissue, that can form, are thought to be related to primitive streak remnants, which ordinarily disappear.
First arch syndrome
First arch syndromes are congenital defects caused by a failure of neural crest cells to migrate into the first pharyngeal arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are structures seen in the embryonic development of verte ...
s are congenital disorder
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
s of facial deformities, caused by the failure of neural crest cells to migrate to the first pharyngeal arch.
Spina bifida
Spina bifida (Latin for 'split spine'; SB) is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the spine and the membranes around the spinal cord during early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, me ...
a congenital disorder
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
is the result of the incomplete closure of the neural tube.
Vertically transmitted infection
A vertically transmitted infection is an infection caused by pathogenic bacteria or Pathogenic virus, viruses that use mother-to-child transmission, that is, Transmission (medicine), transmission directly from the mother to an embryo, fetus, or ...
s can be passed from the mother to the unborn child at any stage of its development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
* Photograph ...
.
Hypoxia a condition of inadequate oxygen supply can be a serious consequence of a preterm
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between ...
or premature birth.
See also
*Embryo loss
Embryo loss (also known as embryo death or embryo resorption) is the death of an embryo at any stage of its development which in humans, is between the second through eighth week after fertilization. Failed development of an embryo often results i ...
* Aorta-gonad-mesonephros
The aorta-gonad-mesonephros (AGM) is a region of embryonic mesoderm that develops during embryonic development from the para-aortic splanchnopleura in chick, mouse and human embryos. The very first adult definitive haematopoietic stem cells, capa ...
* CDX2
* Development of the reproductive system
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically ...
* Development of the urinary system
* Developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and di ...
* Drosophila embryogenesis
''Drosophila'' embryogenesis, the process by which ''Drosophila'' (fruit fly) embryos form, is a favorite model system for genetics and developmental biology. The study of its embryogenesis unlocked the century-long puzzle of how development ...
* Embryomics
* Gonadogenesis
* Human tooth development
Tooth development or odontogenesis is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth. For human teeth to have a healthy oral environment, all parts of the tooth must develop during appropriate stag ...
* List of human cell types derived from the germ layers
This is a list of cells in humans derived from the three embryonic germ layers – ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
Cells derived from ectoderm
Surface ectoderm Skin
* Trichocyte
* Keratinocyte
Anterior pituitary
* Gonadotrope
* Corticotro ...
* Potential person
* Recapitulation theory
The theory of recapitulation, also called the biogenetic law or embryological parallelism—often expressed using Ernst Haeckel's phrase "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny"—is a historical hypothesis that the development of the embryo of an ani ...
* The Human Embryo
Additional images
References
External links
Virtual human embryo
Photo of blastocyst in utero
* Slideshow
In the Womb
{{DEFAULTSORT:Human Embryogenesis Embryology Human biology